Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain platform that enables the creation and deployment of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). It was first proposed in 2013 by Vitalik Buterin, a programmer and cryptocurrency researcher, and was launched in 2015.
Ethereum is designed to be a more flexible and versatile blockchain platform than Bitcoin, which was the first cryptocurrency and blockchain platform. While Bitcoin’s main purpose is to serve as a digital currency, Ethereum’s primary focus is on providing a platform for building decentralized applications that can execute complex logic and automate business processes through the use of smart contracts.
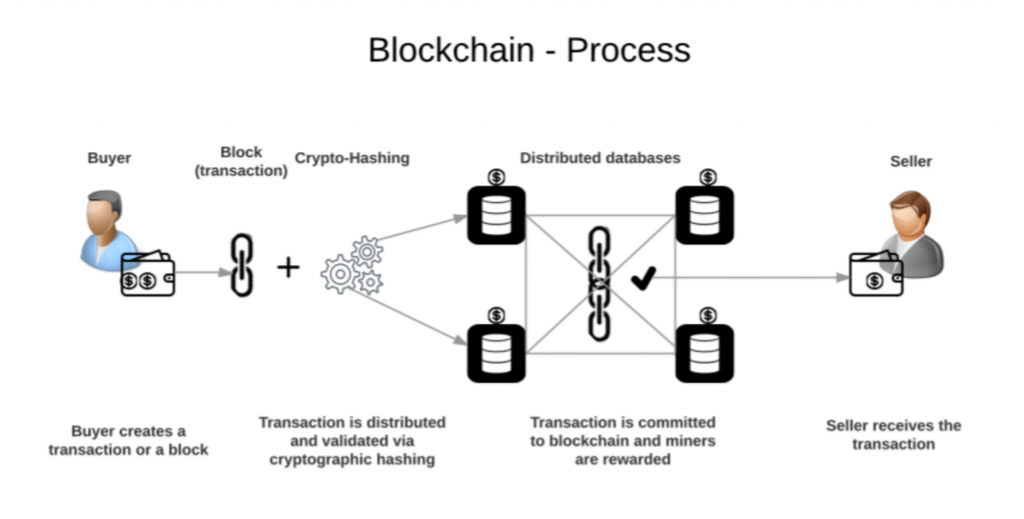
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code. They allow for the automation of complex business processes and the creation of new types of applications that can operate in a decentralized and trustless environment.
Ethereum uses a cryptocurrency called Ether (ETH) as its native currency, which is used to pay for transaction fees and to incentivize network participants to maintain and secure the network. Ethereum’s decentralized nature also means that it is not controlled by any central authority, making it resistant to censorship and manipulation.

How its different from bitcoin
Ethereum is a blockchain platform for building decentralized applications and executing smart contracts, while Bitcoin is primarily a digital currency and store of value. Ethereum has a more advanced scripting language, uses a gas system for transactions, and has a more flexible governance structure than Bitcoin.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Ethereum is a blockchain platform designed for building decentralized applications and executing smart contracts.
- Bitcoin is primarily a digital currency and store of value, with a simpler scripting language and transaction system than Ethereum.
- Ethereum’s more advanced scripting language allows for the creation of more complex smart contracts and dApps.
- Ethereum uses a gas system to pay for computational resources needed to execute smart contracts and dApps.
- Ethereum has a more flexible governance structure than Bitcoin, with a foundation and council of stakeholders making decisions about the platform’s future direction.
How Does Ethereum Work?
Ethereum is a blockchain platform that enables the creation and execution of smart contracts and decentralized applications. It works through a network of computers running the Ethereum software, which form a decentralized ledger or blockchain. Transactions on the network are validated and added to the blockchain through a process called mining, and the network uses a system called gas to pay for the computational resources needed to execute smart contracts and other operations. Smart contracts are self-executing programs that automatically enforce the terms of a contract, and they can be used to automate complex business processes and create new types of decentralized applications. Ethereum’s decentralized nature makes it resistant to censorship and manipulation, and its flexibility and versatility make it a popular platform for developers looking to build decentralized applications and execute complex operations in a secure and transparent manner.
How Can I Buy Ethereum?
You can buy Ethereum through a cryptocurrency exchange or brokerage. The process typically involves creating an account, verifying your identity, and funding your account with a bank transfer, credit card, or other payment method. Once your account is funded, you can place an order to buy Ethereum at the current market price or a specific price of your choosing. After the purchase is complete, you can store your Ethereum in a digital wallet, which can be a hardware wallet, software wallet, or online wallet provided by the exchange. It’s important to research the exchange or brokerage you plan to use and take appropriate security measures to protect your funds.
How Does Ethereum Make Money?
Ethereum makes money primarily through the appreciation of its native cryptocurrency, Ether (ETH), which is used to pay for transactions on the network and incentivize miners to validate transactions and create new blocks on the blockchain. Ethereum also generates revenue through transaction fees, which are paid in Ether and are used to compensate miners for their computational resources. In addition, the Ethereum Foundation, a non-profit organization that supports the development and growth of the Ethereum platform, relies on donations and grants from individuals, organizations, and companies to fund its operations.
Is Ethereum a Cryptocurrency?
Yes, Ethereum is a cryptocurrency. It has its own native digital currency, Ether (ETH), which is used to pay for transactions on the Ethereum network and incentivize miners to validate transactions and create new blocks on the blockchain. Ether is also used as a means of exchange and store of value, similar to other cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. However, Ethereum is more than just a cryptocurrency, as it also provides a platform for the creation and execution of smart contracts and decentralized applications.
Can Ethereum Be Converted to Cash?
Yes, Ethereum can be converted to cash through various cryptocurrency exchanges and brokerage services. These services allow you to sell your Ethereum for a fiat currency such as US dollars, euros, or other currencies, which can then be withdrawn to a bank account or other payment method. The process typically involves creating an account with a cryptocurrency exchange or brokerage, verifying your identity, and placing a sell order for your Ethereum at the current market price or a specific price of your choosing. Once the sale is complete, the cash proceeds can be withdrawn to a bank account or other payment method.
Difference between Ethereum & Ethereum Classic

| Ethereum | Ethereum Classic |
|---|---|
| Started as a hard fork from the original Ethereum blockchain in 2015 | The original Ethereum blockchain that remained unchanged after the hard fork |
| Supports the use of smart contracts and decentralized applications (Dapps) | Also supports smart contracts and Dapps |
| Has a larger community, higher market capitalization, and higher transaction volume | Has a smaller community, lower market capitalization, and lower transaction volume |
| Uses a proof-of-work consensus algorithm, but is moving towards a proof-of-stake algorithm | Uses a proof-of-work consensus algorithm |
| Has a more centralized governance structure, with decisions made by the Ethereum Foundation and core developers | Has a more decentralized governance structure, with decisions made by the community through a consensus process |
| Has undergone multiple upgrades, including the recent Ethereum 2.0 upgrade, which aims to improve scalability and security | Has not undergone any major upgrades since the hard fork |
| Has a larger developer community and more active development, with many new Dapps and projects being built on the platform | Has a smaller developer community and less active development, with fewer new Dapps and projects being built on the platform |